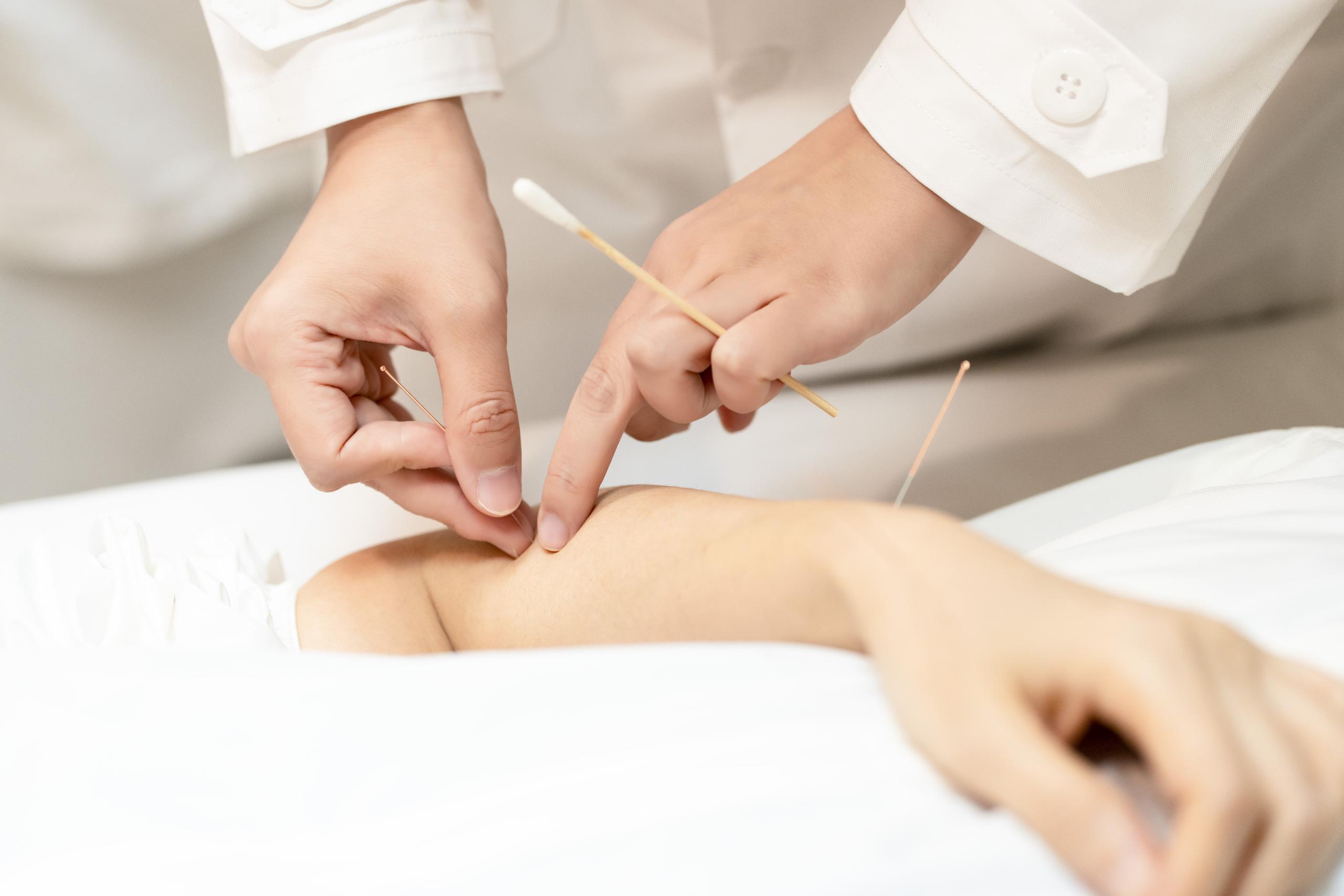
1. Basic Concepts
Acupuncture is an essential component of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). It involves stimulating specific acupoints to regulate qi and blood, balance yin and yang, and thereby treat diseases and promote health.
2. Treatment Principles
- Meridian Theory: Acupuncture is based on the meridian system, which is believed to be the pathway for the flow of qi and blood, connecting the entire body.
- Acupoints: Acupoints are key locations on the meridians. Stimulating these points can regulate the functions of related internal organs.
- Harmonizing Qi and Blood: Acupuncture works by regulating qi and blood to restore the balance of yin and yang, achieving therapeutic effects.
3. Treatment Tools
- Acupuncture Needles: Typically made of stainless steel, with varying lengths and thicknesses chosen based on treatment needs.
- Moxa Sticks: Used in moxibustion, where burning mugwort is used to warm and stimulate acupoints.
4. Treatment Methods
- Needling: Inserting needles into acupoints and applying techniques like lifting, thrusting, and twisting to create stimulation.
- Moxibustion: Burning moxa sticks to apply heat stimulation to acupoints.
- Electroacupuncture: Applying a mild electric current to the needles to enhance stimulation.
- Cupping: Using suction cups to create negative pressure on the skin, promoting blood circulation.
5. Indications
- Pain Management: Such as headaches, joint pain, and lower back pain.
- Internal Diseases: Such as digestive and respiratory disorders.
- Neurological Disorders: Such as post-stroke conditions and facial paralysis.
- Gynecological Issues: Such as irregular menstruation and dysmenorrhea.
- Others: Such as insomnia, anxiety, and obesity.
6. Treatment Process
- Diagnosis: Determining the cause of the condition and the treatment plan through observation, listening, questioning, and pulse diagnosis.
- Treatment: Selecting acupoints and treatment methods based on the diagnosis.
- Course of Treatment: Typically requires multiple sessions, with the exact number depending on the condition.
7. Precautions
- Choose a Qualified Practitioner: Ensure the treatment is safe and effective.
- Communication Before Treatment: Inform the practitioner of your health status and any allergies.
- Post-Treatment Care: Avoid strenuous exercise and rest appropriately.
8. Contraindications
- Infections and Skin Conditions: Avoid acupuncture on infected or affected skin areas.
- Bleeding Disorders: Patients with conditions like hemophilia should proceed with caution.
- Pregnant Women: Certain acupoints may induce miscarriage and require special attention.
9. Research and Development
The efficacy of acupuncture has been confirmed by numerous studies and is gradually being integrated into modern medical systems. Many countries have included it in their health insurance coverage.
Summary
Acupuncture is an effective TCM treatment method that regulates qi and blood by stimulating acupoints, treating a variety of diseases. Treatment should be performed by a qualified practitioner, with attention to relevant contraindications and post-treatment care.